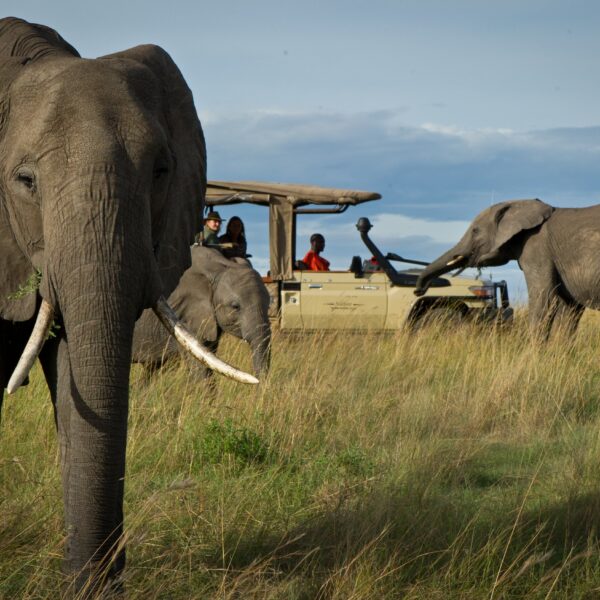
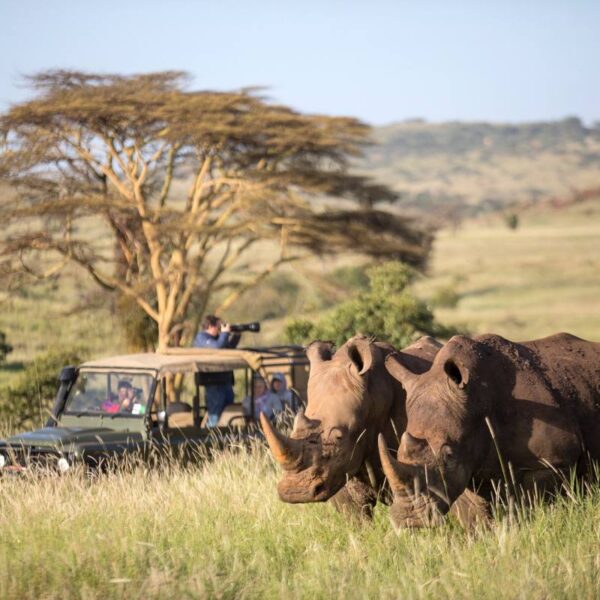
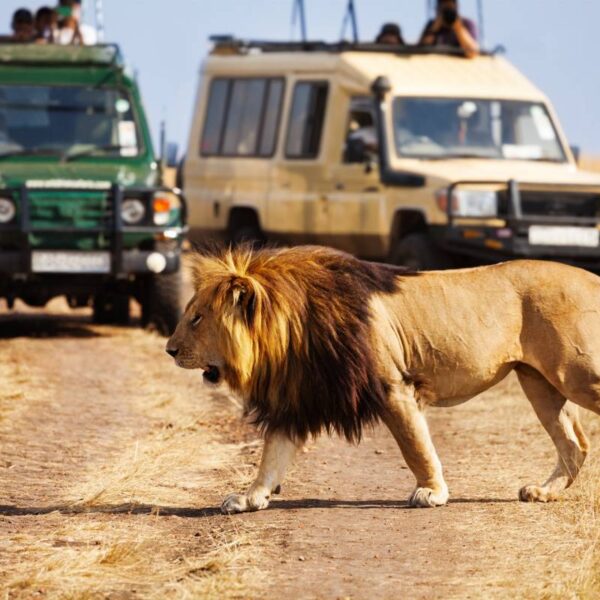
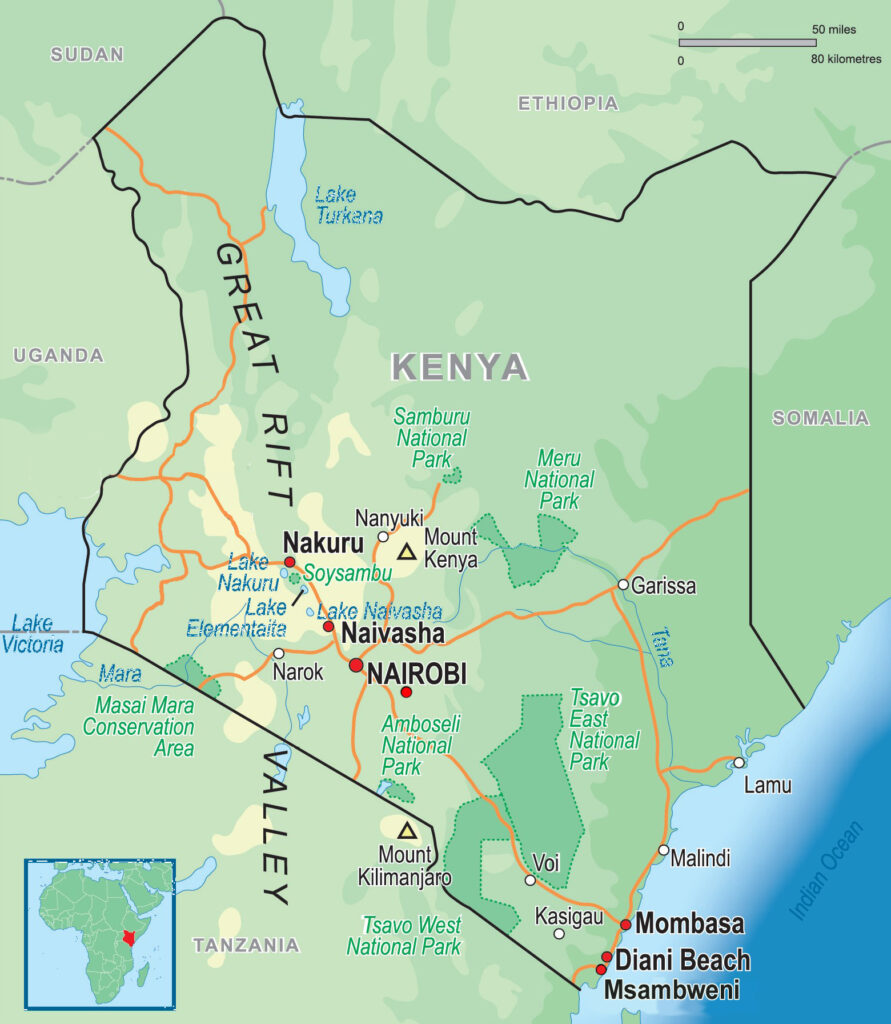
Kenya covers an area of 586,600 square kilometers (226,487 square miles) and is approximately the size of the state of Texas. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Somalia, Uganda and Tanzania. The population over 55,000,000 people.
The Kenyan coast extends for 480 km (298 mi) along the Indian Ocean. The beaches along the coast are protected from ocean waves by coral fringe and barrier reefs. This area of Kenya is famous for mangrove swamps, rocky inlets and palm trees. Areas around the coast are also ideal for sugar cane plantations as the land is narrow, low-lying and fertile.
The interior consists of a plateau beyond the coastal plain that rises to the central highlands in the south and continues through Ethiopia in the north. The interior is made up of vast arid and semi-arid zones with few low valleys characterized by sparse savannah, thorn trees and scrub. Due to the aridity of the region, it is not fertile and does not support agriculture. As a result of this, the interior is very sparsely populated.
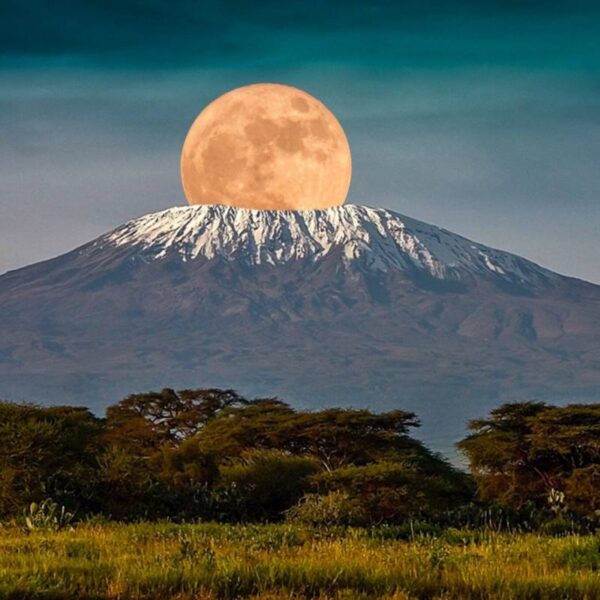
The Great Rift Valley runs north to south almost the entire length of Kenya. It is home to many freshwater and alkaline lakes. The Aberdare Mountains and Mount Kenya border the Rift Valley to the east and to the west is the Mau Escarpment. The eastern Highlands have been cultivated by Europeans and Kenyans alike and are characterised by savannah grassland, deep green valleys, narrow canyons and steep rugged mountains. Located in central Kenya, just south of the equator, Mount Kenya at 5,199 m (17,057 ft) is the second tallest mountain in Africa after Kilimanjaro and is the source of the country’s name. Six mountains (including Mount Kenya) reach elevations over 3,000 m (9,842.5 ft).
Western Kenya is made up of a plateau that runs the length of the country. The land here is especially fertile due to lava deposits and volcanic activity that has fortified the soil over the years. Lake Victoria, the world’s second-largest lake is located on the western slope of the Great Rift Valley. The land around Lake Victoria and the surrounding hills of Kakamega is home to a great deal of wildlife as well as tropical forests.